Apr 01, 2025
Car Depreciation Guide: Formula, Calculate, Examples, Rates & Tips
Apr 09, 2025
As soon as you buy or lease a car and drive it off the dealer's lot, its value immediately begins to drop. The difference between the amount you paid for the car and the value at which it will be valued at a particular point in time is called depreciation.
When you lease a vehicle, you pay depreciation plus interest and taxes. The rate of depreciation will determine the residual value, which directly affects your monthly payments when leasing. Depreciation is the basis for calculating your monthly payments, and it is what is divided by the number of months. Therefore, you should definitely be aware of how fast depreciation is, what it depends on, how to calculate it, and whether it can be reduced.
The main issues addressed in the article are:
- What is depreciation
- Why the value of an automobile decreases
- The rate of depreciation per year
- What factors affect auto depreciation
- How to calculate depreciation on a car
- Car Depreciation Example
- How to reduce depreciation
What Is Car Depreciation?
Depreciation is the decrease in value due to wear and tear or constant use. It is invisible, but it affects absolutely every vehicle. New car or used, it loses value with each passing year. Knowing how quickly a car depreciates will help you make a more informed decision whether to lease or buy it, as well as determine the best length of time to use the vehicle.
Depreciation is the biggest cost of ownership. The more years a car lasts and the more miles driven on it, the cheaper its price, but that's not all the factors that determine the rate of depreciation. It also depends on market conditions, demand, new models, technology, availability of parts for repair and modernization.
A new car can lose up to 60% of its value in the first 3 years (depreciation rate is 40%). Further this process slows down. A used car will have lower depreciation costs.
Imagine that 5 years ago you bought (or borrowed) a Mazda CX-5 for $40,000. Even if you invested a few thousand dollars more in it and added accessories, you won't be able to get the full amount of money back for the car. If you sold it now for $24,000, you'd lose 40% of its value. That is a loss of $16,000 for the time you have been operating the vehicle.
Why Do Cars Lose Value?
Several factors cause your car’s value to decline over time:
- Usage and Mileage: The more often you drive and the higher the odometer reading, the lower your car’s resale value.
- Mechanical Condition: When you trade in or sell your vehicle, its condition will be assessed. Signs of wear and tear, accident damage, poor repairs, or aftermarket parts can all reduce its market value.
- Fuel Prices: Gas prices fluctuate, and when fuel becomes more expensive, less efficient cars tend to lose value faster.
- Market Demand: Consumer preferences change. In some years, SUVs and crossovers are hot; in others, compact and fuel-efficient cars are in higher demand.
- Make and Model: Brand reputation matters. Some cars hold their value better than others due to reliability, build quality, or lower long-term maintenance costs.
How Much Does a Car Depreciate Per Year?
A new car becomes a used car the moment it’s purchased. Within the first year, its value typically drops by about 19–20%. In the following four years, the average annual depreciation is around 10–15%. An approximate car depreciation chart looks like the one shown in the image.
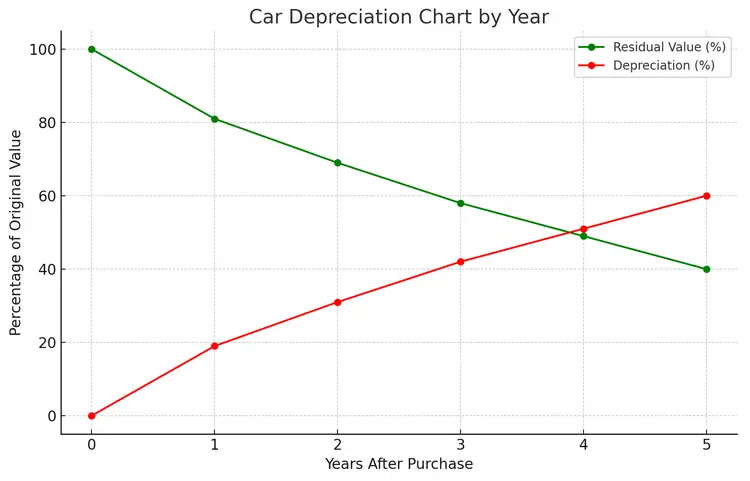
Below is a year-by-year car depreciation table showing how much value a vehicle loses each year and how that affects its residual value (based on MSRP):
| Year of Ownership | Annual Depreciation (%) | Cumulative Depreciation (%) | Residual Value (% of MSRP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20% | 20% | 80% |
| 2 | 15% | 32% | 68% |
| 3 | 13% | 41% | 59% |
| 4 | 11% | 48% | 52% |
| 5 | 10% | 54% | 46% |
- Annual depreciation shows how much value the car loses during a specific year.
- Cumulative depreciation reflects how much of the original price the vehicle has lost by a given year.
- Residual value indicates how much of the original value remains.
Example: If a car cost $40,000, after 3 years it would be worth about 59% of its MSRP, or $23,600.
Factors That Affect Car Depreciation
There are two types of factors that can influence how much a car wears out and, consequently, how much it depreciates. The first type can be influenced by the owner; the second relates to external conditions. You should be aware of them if you want to reduce your vehicle’s depreciation:
Mileage. Cars with higher mileage sell for significantly less because covering long distances leads to greater wear on mechanical components.
Maintenance. Timely, regular, and professional servicing helps keep parts in good condition longer, which means a longer lifespan and lower depreciation.
Physical condition. Any damage resulting from accidents affects both appearance and technical condition. A vehicle used only for commuting or leisure will show much less wear than one regularly used for work or in tough conditions.
Warranty coverage. A car that’s still under warranty has greater resale value. It seems more reliable and poses less risk for the buyer.
Age. The older the car, the cheaper it is (with the exception of classic cars).
Make/model and popularity. Models that have remained in demand over time are valued more highly than less popular ones.
Exterior color. Paint can often influence depreciation. Classic colors like black or gray reduce depreciation more than custom paint jobs.
We recommend reviewing all of these factors so you don’t face unnecessary financial issues after purchasing a car. We’ll look at which cars hold their value best — and which depreciate the most — in a separate article.
How Is Car Depreciation Calculated?
There are several ways to calculate vehicle depreciation — online market value estimation tools, as well as a depreciation formula you can use to estimate how much value your car has lost. To make the calculation, you’ll need to know:
- The current market value of the car (you can check prices on classified sites for similar models or use appraisal services);
- The purchase price;
- Any amount of initial costs, fees, and taxes;
- The car’s age (how many years have passed since the purchase);
- The annual depreciation rate (you can use an average of 14%).
You won’t be able to get an exact number using a basic formula, but it’s good enough for a general estimate.
Car Depreciation Formula
Car depreciation is calculated using the following equation:
Depreciation (D) = Purchase Price (P) − Current Market Value (A)
How to Estimate Depreciation Over 5 Years
To make an approximate estimate of your car’s value in a few years, use the following formula:
A = P × (1 − R/100)ⁿ.
Where:
- A is the future value (after n years);
- P is the original purchase price;
- R is the annual depreciation rate (remember, the value drops by 20% in the first year, then by 10–15% annually after that);
- n is the time that has passed since purchase (in years).
After gathering all the necessary data, you can calculate the estimated depreciation rate of the vehicle.
But keep in mind, this is an exponential depreciation model, which not all experts consider accurate. It’s a simplified method used only for rough estimates. In reality, a car’s value decreases unevenly over time.
Car Depreciation Calculation Example
The easiest way to see how this works is to look at a real example. Let’s go back to the previously mentioned Mazda CX-5 with a purchase price of $40,000. After applying the formula, we get the following equation:
40,000 × (1 − 14/100)⁵
After calculation, the approximate value of the car after 5 years is $18,800.
Depreciation in this case is:
$40,000 − $18,800 = $21,200
If you’re looking for more than just an approximate estimate of your car’s value, use a car depreciation calculator (you can find them on sites like Kelley Blue Book or Edmunds), or consult a tax professional. The calculation will be much more accurate if it takes into account the make and model, year of manufacture, mileage, and current value.
How to Reduce the Rate of Vehicle Depreciation
Choose a car with a high residual value — they retain value better. Also, opt for popular brands — their resale value tends to be higher. In addition:
- Don’t neglect car care and regular maintenance. It makes the vehicle more reliable.
- Store the car in a garage instead of outdoors. Rain, snow, and UV rays (especially hail) negatively affect the paintwork.
- Avoid modifications. Yes, they might look attractive, but they often reduce resale value.
- Minimize mileage. A high mileage limit reduces the resale price.
FAQ
How does mileage affect vehicle depreciation?
Higher mileage means more wear and tear. The lower the mileage, the higher the value. A car with fewer miles is generally perceived as more reliable and longer-lasting.
Do hybrids or regular cars depreciate faster?
According to a study by iSeeCars, on average, hybrids and electric vehicles depreciate faster due to rapidly changing technology and the scale of their production. However, each case and brand/model should be considered separately — for example, Tesla, Toyota Prius, and some others may be exceptions.